A posterior labrum tear refers to the tearing or damage of the cartilage ring surrounding the socket of the shoulder joint. It can disrupt shoulder stability and function. The posterior labrum plays a crucial role in stabilizing the shoulder joint by deepening the socket and providing support to the upper arm bone. Its integrity is essential for smooth shoulder movement.
This blog will cover the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for posterior labrum tears. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of this condition, including preventive measures and the importance of shoulder health.
Shoulder Joint Anatomy

Shoulder Joint Structure
The shoulder joint is a highly mobile joint formed by the articulation of three bones: the humerus (upper arm bone), scapula (shoulder blade), and clavicle (collarbone). It is a ball-and-socket joint, allowing for a wide range of motion in different directions. A 'ball' at the top of the upper arm bone (the humerus) fits neatly into a' socket', called the glenoid, which is part of the shoulder blade (scapula).
Role of the labrum
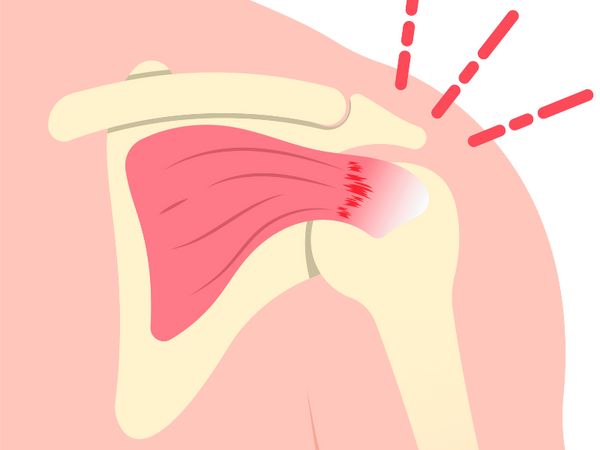
The labrum is a fibrous ring of cartilage that surrounds the shoulder socket, called the glenoid. It serves as a stabilizing structure, deepening the socket and providing a supportive rim that provides support for the shoulder joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. The biceps tendon is a long, cord-like structure that attaches the biceps muscle to the shoulder and helps stabilize the joint.
It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. The labrum helps maintain the stability of the shoulder joint, particularly during dynamic movements and overhead activities. The labrum helps keep your shoulder joint in place. It also serves as an attachment point for many of the ligaments of the shoulder, as well as one of the tendons from the biceps muscle in the arm.
Posterior Labrum Functions
Enhancing shoulder stability: The posterior labrum provides additional support to the joint, preventing excessive movement or dislocation of the humeral head.
Shock absorption: The labrum acts as a cushion, absorbing shock and reducing stress on the joint during activities.
Load transmission: It aids in the transfer of forces between the upper arm bone and the shoulder socket, optimizing joint function and minimizing wear and tear.
Types of Shoulder Labral Tears
The two most common types of labral injuries in the shoulder are SLAP tears and Bankart tears (also known as Bankart lesions).
SLAP tear
SLAP stands for "superior labrum from anterior to posterior." A SLAP tear often causes pain at the front of the shoulder near the biceps tendon. There are several different types of SLAP tears. Your surgeon will determine how best to repair your SLAP injury once he or she sees it fully during arthroscopic surgery. This may require simply removing the torn part of the labrum, or reattaching the torn part using stitches.
SLAP tears can be caused by falling onto an outstretched hand, quickly lifting a heavy object or from a forceful, overhead arm motion.
Bankart tear:
Also known as Bankart lesion or anterior glenoid labral lesion, is a tear in the lower rim of the shoulder's labrum. It's often caused by an interior shoulder dislocation, which occurs when the humeral head moves out of the front of the socket. The tear can also occur in the back part of the socket, which is called a posterior labral tear. A dislocated shoulder that causes a Bankart tear can occur during sports activity or trauma, such as a fall.
Bankart tears typically occur with shoulder dislocation and are more frequent in younger athletes than in older athletes. Shoulder dislocation can occur during a collision in contact sports such as football, hockey, or basketball.
Causes of Posterior Labrum Tears

Traumatic injuries (e.g., falls, dislocations)
Posterior labrum tears can occur as a result of acute traumatic events, such as falls onto an outstretched arm or direct impact to the shoulder. Dislocations, where the humeral head is forced out of the socket, can also lead to a shoulder labral tear.
Repetitive overhead activities
Engaging in repetitive overhead motions, such as those involved in sports like swimming, tennis, or baseball, can contribute to a posterior labrum tear. The repetitive stress and strain on the shoulder joint over time can lead to labral damage.
Sports-related injuries
Sports that involve contact, collisions, or sudden changes in direction can increase the risk of posterior labrum tears. Sports like football, rugby, and martial arts where the shoulder can be subjected to forceful impacts are particularly associated with such injuries.
Degenerative changes and aging
With age, the labrum can naturally degenerate and become more susceptible to tears. The wear and tear of daily activities, coupled with the natural aging process, can gradually weaken the labrum, making it more prone to tears.
Symptoms and Signs

Shoulder pain and discomfort
One of the most common symptoms of a posterior labrum tear is persistent shoulder pain. The pain is often localized to the back of the shoulder joint and may worsen with certain movements or activities. The intensity of the pain can vary from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the tear.
Decreased range of motion
Individuals with a posterior labrum tear may experience a decreased range of motion in their shoulder. They may find it difficult to fully raise their arm or perform overhead movements. The tear can restrict the smooth gliding motion of the joint, leading to stiffness and limited mobility.
Sensation of instability or "catching" in the shoulder
A posterior labrum tear can result in a feeling of shoulder instability. Individuals may describe a sensation of the joint "catching" or popping, especially during certain movements. This feeling of instability can affect their confidence and ability to engage in physical activities.
Weakness or loss of strength
Due to the compromised stability and function of the shoulder joint, individuals with a posterior labrum tear may experience weakness or a loss of strength in the affected shoulder. This can make it challenging to perform everyday tasks or engage in activities that require upper body strength.
Diagnosis

Patient history and physical examination
The diagnosis of a posterior labrum tear begins with a comprehensive patient medical history. The healthcare provider will inquire about the onset of symptoms, any relevant traumatic events or repetitive activities that may have caused the injury, and the nature and intensity of the symptoms. A thorough physical examination of the shoulder will be performed, assessing range of motion, stability, and any signs of tenderness or abnormalities.
Imaging tests (e.g., MRI scan, CT scan)
To confirm the diagnosis, imaging tests are often utilized. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI scan) is commonly employed as it provides detailed images of the shoulder joint and can reveal labral tears, as well as any associated structural abnormalities or soft tissue injuries that occur from acute trauma or repetitive shoulder motion. In some cases, a Computed Tomography (CT) scan may be recommended to further evaluate the extent of the tear or assess bony structures. In both instances, a contrast medium may be injected to help detect tears.
Arthroscopic evaluation
The surgical technique most commonly used for repairing a SLAP injury is arthroscopy. Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure where your surgeon inserts the arthroscope and small instruments into your shoulder joint, allowing for direct visualization of the shoulder joint. In arthroscopic surgery for SLAP tears, your surgeon examines the labrum and the biceps tendon, which enables the surgeon to assess the tear, determine its size and location accurately, and address any associated issues if needed.
Most patients do not experience complications from shoulder arthroscopy. As with any surgery, however, there are some risks. These are usually minor and treatable.
Treatment Options

The choice of treatment approach depends on the severity of the tear, the individual's symptoms, and their functional goals. Both conservative and surgical options aim to alleviate pain, restore shoulder stability, and improve overall function. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for a posterior labrum tear.
Conservative approaches
In many cases, nonsurgical methods are effective in relieving symptoms and healing the injured structures. If these nonsurgical measures are insufficient, or if the symptoms return, your doctor may recommend surgery. Nonsurgical methods are effective in relieving symptoms and healing the injured structures. If these nonsurgical measures are insufficient, or if the symptoms return, your doctor may recommend surgery.
1. Rest and activity modification
Resting the shoulder and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms are often recommended initially. Modifying activities that put stress on the shoulder can help prevent further damage and promote healing.
2. Physical therapy exercises for strengthening and flexibility
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the conservative management of posterior labrum tears. Specific exercises are prescribed to strengthen the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint, improve flexibility, and enhance stability. This can help compensate for the weakened labrum and promote functional recovery.
3. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain management
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may be prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with a posterior labrum tear. These medications can help manage symptoms while the shoulder heals.
4. CBD oil for pain management
CBD has become a popular and natural remedy for various ailments and conditions, including pain management. While there are many different types of pain that can be treated with CBD, one particularly troublesome type that can greatly benefit from its use is a posterior labrum tear.
Posterior labral tears are a type of injury that can cause intense pain and discomfort, often requiring surgical intervention. Fortunately, research has shown that CBD can be both a safe and effective way to alleviate this type of pain without the need for invasive procedures. By targeting inflammation and calming the nervous system, CBD can provide relief for those suffering from a posterior labrum tear, enabling them to better manage their shoulder pain and regain their quality of life.
Surgical interventions
1. Arthroscopic labral repair
For more severe or symptomatic posterior labrum tears, arthroscopic labral repair may be recommended. This can be done with an incision on the front of the shoulder, or it can be done with arthroscopic techniques through smaller incisions.
During this minimally invasive surgical procedure, the torn labrum is reattached to the glenoid using sutures or anchors. In this procedure, the torn labrum is reattached to the rim of the bone using anchor sutures, along with tightening of the capsules and ligaments. This helps restore stability and function to the shoulder joint.
2. Labral debridement or resection
In some cases, if the tear is less extensive or repair is not feasible, labral debridement or resection may be performed. This involves removing or trimming the damaged portion of the labrum to alleviate symptoms and improve shoulder function.
3. Rehabilitation and post-surgical care
Following surgical intervention, a comprehensive rehabilitation program is essential for optimal recovery. Physical therapy focuses on restoring the range of motion, strength, and stability of the shoulder joint. Gradually, functional exercises and activities are introduced to ensure a safe and successful return to normal daily activities and sports.
Rehabilitation and Recovery

Rehabilitation and recovery are integral components of the treatment process for a posterior labrum tear. By diligently following the rehabilitation program, individuals can optimize their healing, regain strength and function, and safely return to their desired activities. Regular communication with the healthcare team is essential to monitor progress, address concerns, and ensure a successful recovery journey.
Rehabilitation after surgery
Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the recovery process following surgical intervention for a posterior labrum tear. It aims to restore range of motion, strength, stability, and functional abilities of the shoulder joint. Rehabilitation helps optimize healing, minimize scar tissue formation, and reduce the risk of complications.
Rehabilitation exercises and protocols
The specific rehabilitation exercises and protocols will vary depending on the individual's condition, the extent of the tear, and the surgical procedure performed. Initially, the focus may be on gentle range-of-motion exercises to prevent stiffness and promote healing. As healing progresses, exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles and improve stability are gradually introduced. The rehabilitation program is typically tailored to the individual's needs and progresses in a phased manner under the guidance of a physical therapist. To control pain and swelling, your physical therapist may use ice, electrical stimulation, massage therapy, and other hands-on treatments.
Timeline for recovery
The timeline for recovery and return to normal activities following a posterior labrum tear and surgical repair can vary. It depends on factors such as the severity of the tear, surgical technique used, individual healing capabilities, and adherence to rehabilitation protocols. In general, the initial recovery period involves protecting the repaired labrum and gradually increasing activity levels under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Full recovery and return to normal activities can range from several weeks to several months, with more strenuous activities or sports requiring a longer timeline.
Potential complications and how to avoid them
While complications following surgical repair of a posterior labrum tear are rare, it is important to be aware of potential risks. Complications can include infection, stiffness, recurrent instability, nerve or blood vessel injury, or failure of the repair. To minimize the risk of complications, it is crucial to strictly adhere to post-operative care instructions, follow the prescribed rehabilitation program, avoid excessive or premature stress on the shoulder, and promptly report any concerns or unexpected symptoms to the healthcare provider.
Preventive Measures

Proper warm-up and stretching routines
Engaging in a thorough warm-up before physical activities or sports that involve the shoulder can help prepare the muscles, tendons, and ligaments for the upcoming movements. Incorporating dynamic stretches that target the shoulder joint and surrounding muscles can enhance flexibility, improve blood flow, and reduce the risk of injury.
Technique improvement and modification
Proper technique and form are essential in preventing posterior labrum tears. Whether participating in sports or performing repetitive activities, it is important to focus on proper body mechanics and technique. Seeking guidance from a coach, instructor, or qualified professional can help identify and correct any faulty movement patterns that may contribute to shoulder injuries.
Strengthening exercises for shoulder stability
Strengthening the muscles around the shoulder joint can improve stability and reduce the risk of a shoulder labral tear. Specific exercises targeting the rotator cuff muscles, scapular stabilizers, and other shoulder muscles can enhance the overall strength and support of the shoulder joint. Incorporating resistance training, such as using resistance bands or weights, can be beneficial in developing shoulder stability.
Avoiding overuse and excessive stress on the shoulder joint
Overuse and repetitive stress on the shoulder joint can increase the likelihood of posterior labrum tears. It is important to listen to your body and avoid excessive or prolonged activities that strain the shoulder. Taking regular breaks, alternating activities, and incorporating rest days into your routine can help prevent overuse injuries. Additionally, pacing yourself during activities and gradually increasing intensity or duration can reduce the risk of excessive stress on the shoulder joint.
Conclusion
In summary, a posterior labrum tear can significantly impact shoulder stability and function. It is important to recognize the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this condition. Posterior labrum tears can occur due to traumatic injuries, repetitive overhead activities, sports-related injuries, or degenerative changes. Symptoms may include shoulder pain, limited range of motion, instability sensations, and weakness.
Diagnosis involves patient history, physical examination, and imaging tests like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scan. In some cases, an arthroscopic evaluation may be necessary for an accurate diagnosis. Treatment options range from conservative approaches, such as rest, physical therapy exercises, and shoulder pain management, to surgical interventions like arthroscopic labral repair or debridement.
Rehabilitation and recovery play a crucial role in the management of posterior labrum tears. Following surgery, a comprehensive rehabilitation program helps restore shoulder function, strength, and stability. Preventive measures, including proper warm-up and stretching, technique improvement, shoulder strengthening exercises, and avoiding overuse, are important for reducing the risk of posterior labrum tears.
If you experience symptoms of a posterior labrum tear, seeking medical evaluation is crucial. By understanding this condition and taking proactive steps towards shoulder health, individuals can make informed decisions and improve their overall well-being.


