Cannabinoids have garnered significant attention in recent years for their potential health benefits and therapeutic properties. Among the diverse array of cannabinoids, Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) emerges as a noteworthy compound with its own unique characteristics and potential applications. As the landscape of cannabis research continues to evolve, understanding the intricacies of cannabinoids like HHC becomes increasingly important.
In this blog post, we delve into the world of HHC, exploring its definition, properties, potential benefits, and implications for health and wellness. Whether you're a curious consumer, a health enthusiast, or a researcher seeking deeper insights, join us on this journey to uncover the mysteries of HHC and its role in the realm of cannabinoids.
Understanding HHC
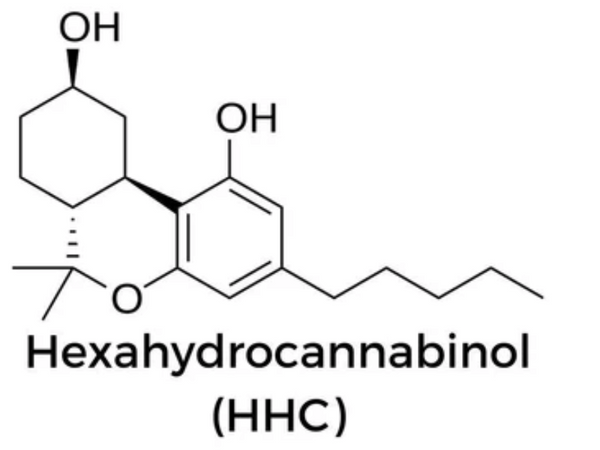
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are both psychoactive cannabinoids derived from the cannabis plant. HHC is a lesser-known cannabinoid found in cannabis and hemp derived cannabinoids, belonging to the same chemical structure as THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (Cannabidiol). While THC is renowned for its potent psychoactive effects, and CBD for its potential therapeutic properties, HHC occupies a unique position with distinct characteristics.
Definition and Chemical Structure
HHC, also known as cyclohexyl-THC, as a hemp derived cannabinoids is a chemical compound derived from the cannabis plant. Its molecular structure includes a cyclohexane ring, which distinguishes it from THC's aromatic benzene ring. This structural variance contributes to differences in its biological activity and effects.
How HHC Differs from THC
Unlike THC, which is predominantly known for its intense psychoactive effects, HHC is believed to have a milder psychoactive profile. While research on the psychoactive effect of HHC is limited compared to THC, preliminary studies suggest that it may produce euphoria and relaxation, albeit to a lesser extent than THC. Additionally, HHC may exhibit different binding affinities to cannabinoid receptor in the endocannabinoid system, leading to varying physiological responses.
Another question that often arises is, “is HHC stronger than THC?” While both cannabinoids can produce psychoactive effect, the HHC high is said to be less intense and more clear-headed than that of THC. Then most people want to know, how long does HHC high last? The duration of the HHC can vary depending on several factors, including dosage, method of consumption, and individual tolerance. Despite being less known, HHC is gradually making its mark in the cannabis industry.
In addition, they offer slightly different benefits that may appeal to consumers seeking specific outcomes, such as milder effects or side effects. Then, there's the fact that THC is readily available in its natural form, while HHC products are much more likely to be synthesized.
In deciding whether to opt for either HHC or THC, potential users should take into account their tolerance levels and desired highs. Different cannabis products offer vastly different experiences, depending on their unique chemical composition. This may be another point of consideration in making an informed decision regarding your HHC or THC consumption.
Potential Benefits and Effects
Although research on HHC is still in its infancy, anecdotal reports and preliminary studies suggest potential benefits and effects. There's a lack of research on how HHC affects the body. Unscientifically, people who have used HHC products report that it has similar effects to THC or cannabis in general.
These may include:
- Relaxation and stress relief

- Mood enhancement

- Appetite stimulation

- Potential anti-inflammatory properties

However, it's essential to note that the evidence supporting these claims is limited, and further research is necessary to elucidate the full spectrum of HHC's effects and therapeutic potential.
The Science Behind HHC
Understanding the scientific mechanisms underlying HHC's effects requires a closer examination of its interaction with the body's endocannabinoid system, (ECS), the complex network of receptors and neurotransmitters responsible for maintaining homeostasis in the body's cannabinoid receptors.
Interaction with the Endocannabinoid System
Like other cannabinoids, HHC interacts with the ECS by binding to cannabinoid receptors, namely CB1 and CB2 receptors. These receptors are distributed throughout the central nervous system and peripheral tissues, playing crucial roles in regulating various physiological processes, including mood, appetite, pain sensation, and immune response.
While THC primarily binds to CB1 receptors, leading to its psychoactive effects, and CBD exhibits minimal affinity for receptors, the specific binding profile of HHC is still being elucidated. Preliminary research suggests that HHC may interact with both CB1 and CB2 receptors, albeit with differing affinities compared to THC.
Research Studies and Findings on HHC
Despite its relative obscurity in cannabis research, a growing body of literature is beginning to explore the pharmacological properties of HHC. Research studies have investigated various aspects of HHC, including its pharmacokinetics, binding affinity to cannabinoid receptors, and potential therapeutic applications.
For example, a recent preclinical study published in the Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics examined the analgesic (pain-relieving) effects of HHC in animal models of neuropathic pain. The study found that HHC administration resulted in dose-dependent reductions in pain behavior, suggesting its potential as a novel analgesic agent.
Legal Status

Is HHC legal? Despite some ads that market HHC as a "legal" type of TCH, it's not entirely clear whether it's against the law to consume it. The 2018 Farm Bill (The Agriculture Improvement Act) appears to allow the use of parts of the high-potency cannabis sativa plant hemp products that contain 0.3% or less of THC.
As with many cannabinoids, the legality of HHC varies significantly depending on jurisdiction and regulatory frameworks. Given its relatively recent emergence in the realm of cannabis research, HHC's legality may not be explicitly addressed in existing cannabis legislation, further complicating its regulatory landscape.
One area of concern for many consumers when it comes to HHC vs. CBD or THC is whether using hemp-derived products is legal. The 2018 Farm Bill separated the hemp plant (defined as cannabis containing 0.3% or less THC) and hemp products from the definition of marijuana in the Controlled Substances Act. This made the cultivation, manufacturing, distribution, possession, and transport of hemp cannabis and its derivatives legal at the federal level.
If you take a drug test, HHC could show up on it—especially if your urine is tested. That's because traces of drugs stay longer in your pee than in your blood. The concentration is also higher. Manmade cannabinoids can show up in your urine 72 hours after you take them.
Current Legal Status
United States: Is HHC legal in the United States? The legal status of HHC remains uncertain due to its novelty and limited regulatory oversight. While federal law prohibits the cultivation and sale of cannabis containing more than 0.3% THC by dry weight, HHC may not be explicitly classified by the federal government as a controlled substance. However, individual states may have their own regulations governing the production, distribution, and consumption of HHC-containing marijuana plants and products.
Other Countries: The legal status of HHC in other countries varies widely, with some nations adopting more lenient cannabis policies allowing for the cultivation and sale of cannabis-derived products, while others maintain strict prohibitionist approaches.
Regulatory Considerations
FDA Regulation: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of cannabis-derived products intended for medicinal or therapeutic use. As HHC gains attention for its potential health benefits, it may fall under the purview of FDA regulation, requiring manufacturers to adhere to stringent quality control standards and undergo clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy.
State-Level Regulations: In states where cannabis is legalized for medical or recreational use, regulatory agencies may establish guidelines for the production, labeling, and sale of cannabinoid receptor HHC-containing products. These regulations aim to ensure consumer safety and product consistency while preventing the diversion of cannabis products into illicit markets.
Potential Medical Uses
While research on HHC is still in its infancy, preliminary studies and anecdotal evidence suggest that this cannabinoid may possess therapeutic potential for various health conditions. Understanding the potential medical uses of HHC requires a comprehensive examination of its pharmacological properties and clinical effects.
Therapeutic Potential for Various Health Conditions
Pain Management

One area of interest is HHC's potential as an analgesic agent for managing pain, particularly neuropathic pain. Preclinical studies have demonstrated HHC's ability to reduce pain behavior in animal models, suggesting its efficacy in alleviating pain symptoms.
Anti-inflammatory Effects

HHC has also shown promise as an anti-inflammatory agent, modulating immune responses and cytokine production in vitro. This anti-inflammatory activity may have implications for treating inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and autoimmune disorders.
Mood Disorders

Given its psychoactive substance, HHC may influence mood and emotional well-being. While further research is needed to elucidate its effects on mood disorders such as anxiety and depression, anecdotal reports suggest that HHC may induce feelings of relaxation and euphoria in some individuals.
Clinical Trials and Evidence-Supporting Medical Use
Despite the limited research on HHC, ongoing clinical trials and observational studies aim to evaluate its safety and efficacy for various medical indications. These studies seek to provide empirical evidence supporting the use of HHC as a therapeutic agent and inform clinical practice guidelines for healthcare professionals.
Additionally, patient-reported outcomes and real-world data may offer valuable insights into HHC's effectiveness and tolerability in diverse patient populations, further shaping its role in medical treatment paradigms.
While the potential medical uses of HHC hold promise, it's essential to approach this emerging cannabinoid with caution and skepticism. Rigorous scientific research, including randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews, is necessary to establish the safety, efficacy, and optimal dosing regimens of HHC for specific health conditions.
Safety and Side Effects
As with any bioactive compound, the use of HHC carries inherent risks and potential side effects that warrant careful consideration. While research on HHC's safety profile is limited, understanding the known risks and adverse effects is essential for promoting responsible use of chemical compounds and minimizing potential harm.
Potential Risks Associated with HHC
Psychoactive Effects

While HHC is often touted for its milder psychoactive profile compared to THC, individuals sensitive to psychoactive compounds may still experience cognitive impairment, altered perception, and changes in mood or behavior after consuming HHC-containing products.
Cardiovascular Effects
Some cannabinoids, including THC, have been associated with transient increases in heart rate and blood pressure, which may pose risks for individuals with preexisting cardiovascular conditions. While data specific to HHC's cardiovascular effects are limited, caution is warranted, especially for those at higher risk of cardiovascular complications.
Respiratory Risks

Inhalation of HHC through smoking or vaporization may expose individuals to respiratory irritants and carcinogens, similar to the risks associated with cannabis smoke. Long-term or heavy use of HHC-containing products via inhalation may increase the risk of respiratory symptoms and respiratory diseases.
Side Effects and Precautions
Cognitive Impairment

Short-term cognitive effects such as impaired memory, concentration, negative effects on productivity, and self-motivation and judgment may occur with HHC use, particularly at higher doses or in susceptible individuals.
Psychiatric Symptom

Some individuals may experience anxiety and paranoia, or hallucinations after consuming HHC, especially in the context of high-dose or uncontrolled use. Individuals with a history of psychiatric disorders should exercise caution when using HHC-containing products.
Dependency and Addiction

While the addictive potential of HHC remains unclear, regular or excessive use may lead to the development of psychological dependence or addiction, particularly in individuals with a history of substance abuse.
Practical Guidelines for Safe Use
Start Low and Go Slow: Begin with a low dose of HHC and gradually increase the dosage as needed while monitoring for adverse effects. This approach allows for individualized dosing and minimizes the risk of overconsumption.
Avoid Mixing with Other Substances: Avoid combining HHC with alcohol or other psychoactive substances, as this may potentiate the effects and increase the risk of unfavorable reactions.
Seek Medical Advice: Consult with a healthcare professional before using HHC, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications that may interact with cannabinoids.
How to Use HHC Safely
Using HHC safely involves not only understanding its potential risks and side effects but also adopting responsible consumption practices. Whether using HHC for its potential therapeutic benefits or recreational purposes, following practical guidelines can help minimize harm and maximize the benefits of this cannabinoid.
Dosage Recommendations
Start with a Low Dose: Begin with the lowest effective dose of HHC and gradually increase the dosage as needed while monitoring your response. This approach allows you to assess your tolerance and sensitivity to HHC's effects while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
Consider Individual Factors: Factors such as age, weight, metabolism, and tolerance to cannabinoids can influence your response to HHC. Adjust your dosage accordingly and pay attention to how your body reacts to different doses.
Methods of Administration
Oral Consumption

Ingesting HHC through oral routes, such as capsules, edibles, or tinctures, provides a convenient and discreet way to consume cannabinoids. However, the onset of effects may be delayed compared to inhalation methods, and bioavailability can vary depending on factors such as in vitro metabolism and digestion.
Inhalation

Inhalation of HHC via smoking or vaporization allows for rapid onset of effects, making it suitable for individuals seeking immediate relief. However, inhalation may pose risks to respiratory health, particularly with long-term or heavy use.
Monitoring Effects and Practicing Moderation
Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body responds to HHC and adjust your dosage or consumption method accordingly. If you experience adverse effects or discomfort, consider reducing your dose or discontinuing use.
Avoid Binge Consumption: Resist the temptation to consume large quantities of HHC in a short period, as this increases the risk of overconsumption and adverse reactions. Instead, practice moderation and consume HHC responsibly.
Creating a Safe Environment
Choose a Comfortable Setting: Consume HHC in a safe and comfortable environment where you feel relaxed and at ease. Avoid unfamiliar or potentially stressful surroundings to minimize the risk of negative experiences.
Stay Hydrated and Nourished: Maintain adequate hydration and nutrition before, during, and after consuming HHC to support your body's physiological functions and mitigate potential side effects.
Seeking Support and Medical Advice

Know When to Seek Help: If you experience severe or persistent adverse effects from HHC use, seek medical attention promptly. Don't hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals or emergency services if needed.
Consult with Healthcare Providers: Before incorporating HHC into your wellness routine, consult with a healthcare provider, particularly if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications that may interact with cannabinoids.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) represents a novel cannabinoid with intriguing potential for both therapeutic and recreational use. While research on HHC is still in its early stages, preliminary studies and anecdotal evidence suggest that this compound may offer unique benefits for individuals seeking relief from pain, inflammation, and mood disorders.
However, the responsible use of HHC requires careful consideration of its potential risks and side effects. From understanding proper dosage and administration methods to practicing moderation and creating a safe environment, incorporating practical guidelines can help mitigate potential harm and maximize the benefits of HHC consumption.
As the scientific understanding of HHC continues to evolve, it's essential for consumers, healthcare professionals, and policymakers to stay informed and engaged. By fostering dialogue, promoting evidence-based research, and implementing sensible regulations, we can navigate the complexities of HHC use and ensure its safe and responsible integration into the realm of health and wellness.
Ultimately, whether exploring the therapeutic potential of HHC or simply seeking to enhance your well-being, prioritizing safety, mindfulness, and informed decision-making is paramount. With responsible practices and a commitment to education, HHC has the potential to enrich lives and contribute positively to the broader landscape of health and wellness.

